Average IQ by Age
IQ (Intelligence Quotient) has long been used as a measure of cognitive ability. While the average IQ is always set at 100, performance can vary across the lifespan. Research shows that our mental abilities do not stay constant: some rise, others stabilize, and eventually decline with age.
How IQ Is Measured by Age
- For children and teens, IQ is age-normed. A 10-year-old’s score is compared only to other 10-year-olds.
- From 18 onwards, scores are compared across the whole adult population. This allows us to see how performance trends shift with age.
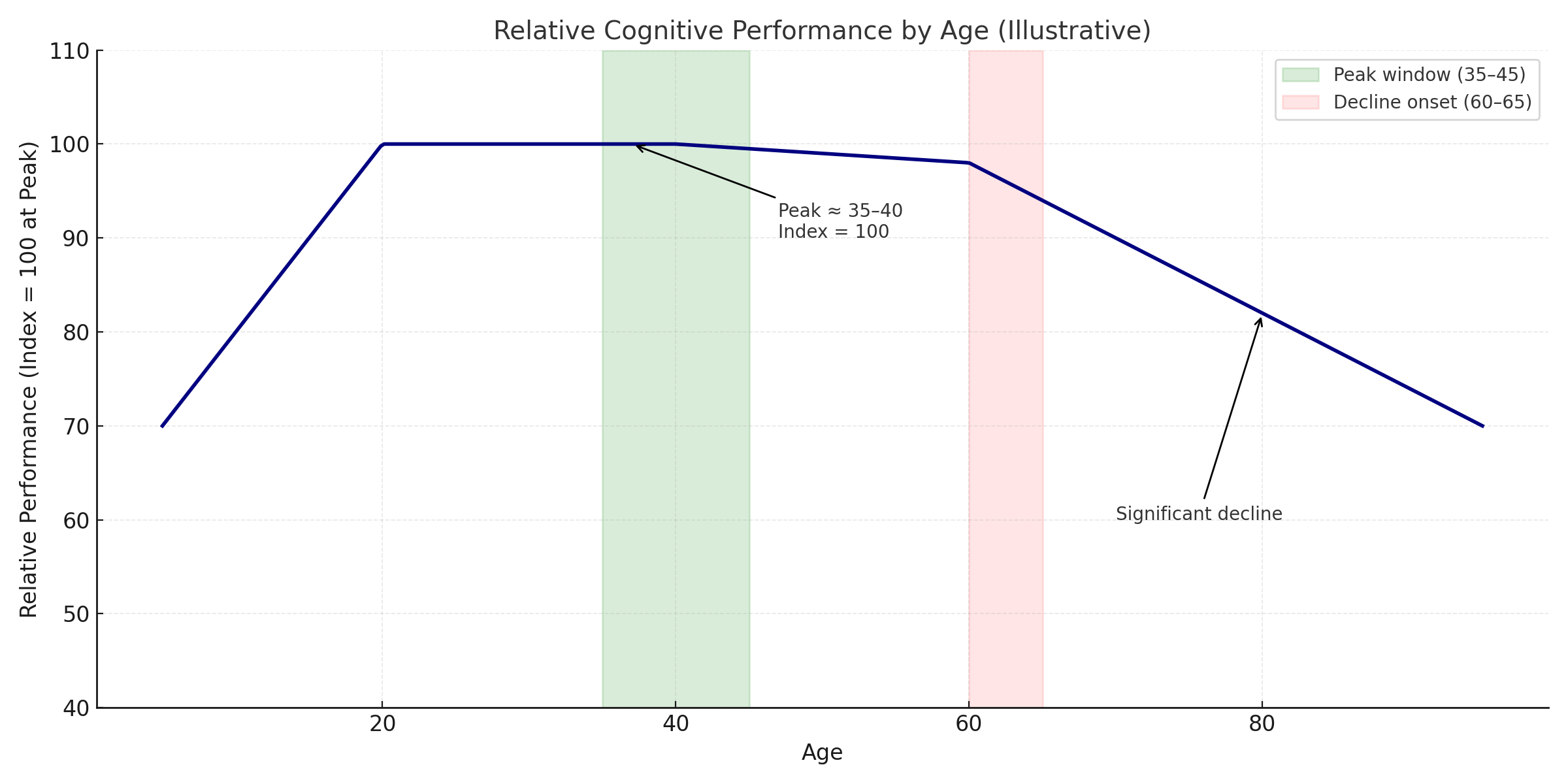
When Does IQ Peak?
Studies and large-scale test data show:
- Rapid growth through childhood and adolescence.
- Peak performance around ages 35–40. This is the period when fluid intelligence (problem-solving, reasoning, processing speed) is at its strongest.
- Stability through the 40s and 50s.
- Gradual decline starts around 60–65, with sharper decreases after 75–80.
Average IQ Performance by Age (Illustrative)
| Age Group | Relative Performance (Index 100 = Peak) |
|---|---|
| Children (5–12) | Growing towards adult baseline (~70–90) |
| Teens (13–19) | Near adult levels (~90–100) |
| Adults (20–40) | Peak performance (~100) |
| Adults (41–59) | Slightly lower (~95–98) |
| Adults (60–75) | Noticeable decline (~85–90) |
| Seniors (76–90) | Significant decline (~60–70) |
(Note: IQ tests are standardized to 100, but this table shows relative trends in test performance.)
Why Does IQ Decline With Age?
Cognitive performance is shaped by many factors:
-
Genetics: Predisposition to longevity and mental sharpness.
-
Brain changes: Processing speed and working memory decline naturally.
-
Health & lifestyle: Sleep, nutrition, exercise, and stress all influence cognition.
-
Education & lifelong learning: People who keep mentally active often slow cognitive decline.
Importantly, crystallized intelligence (knowledge, vocabulary, experience) can remain strong — or even improve — well into older age, even if fluid intelligence declines.
Conclusion
IQ is not fixed. It grows in childhood, peaks in early to mid-adulthood, and gradually declines in later life. This does not mean intelligence disappears — wisdom, creativity, and knowledge often continue to thrive.
